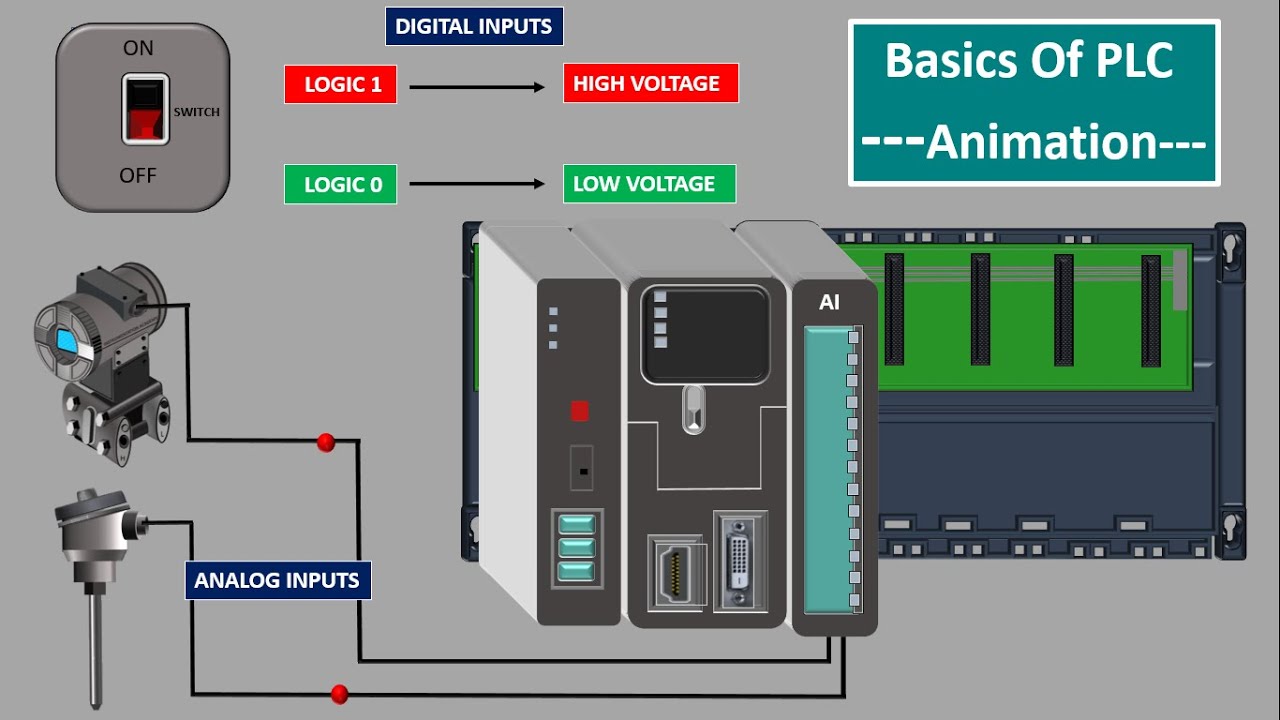
Understanding Inputs and Outputs in PLC Systems
Inputs and outputs are the lifeblood of any Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) system. Inputs capture data from the real world, such as sensor readings or switch positions, while outputs control external devices like motors, valves, and lights. This dynamic interplay between inputs and outputs enables PLCs to automate various industrial processes with precision and efficiency.

The Role of Inputs in PLC Systems
Inputs are essential for PLCs as they provide the necessary information to make informed decisions. Common input devices include sensors, limit switches, and pushbuttons. These components detect changes in the physical environment and transmit corresponding signals to the PLC. By continuously monitoring these signals, the PLC can ascertain the current state of the system and initiate appropriate actions, ensuring seamless operation.
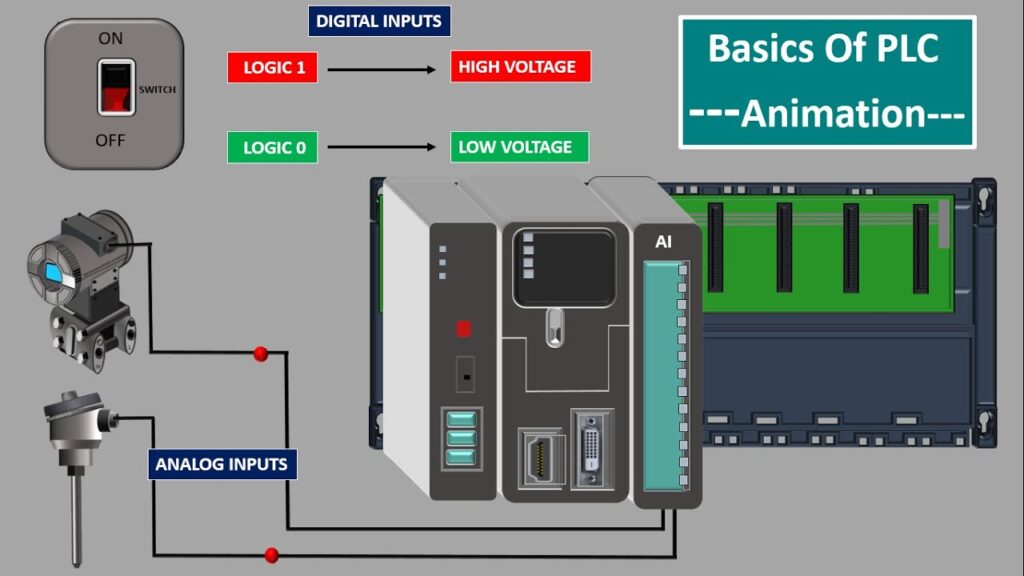
The Role of Outputs in PLC Systems
Outputs are responsible for executing the commands generated by the PLC. These outputs directly interact with the physical world, controlling devices and machinery essential for production processes. Examples of output devices include relays, solenoids, and variable frequency drives. By activating or deactivating these devices, PLCs manipulate the behavior of industrial equipment, thus ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
The Importance of I/O Modules
I/O modules serve as critical interfaces between the PLC and external devices. They provide the electrical connections necessary for data transmission. The selection of I/O modules is influenced by various factors, including the types of devices being controlled, the required voltage levels, and the desired communication protocols. Choosing the right I/O modules is vital to ensure reliable and effective system operation.
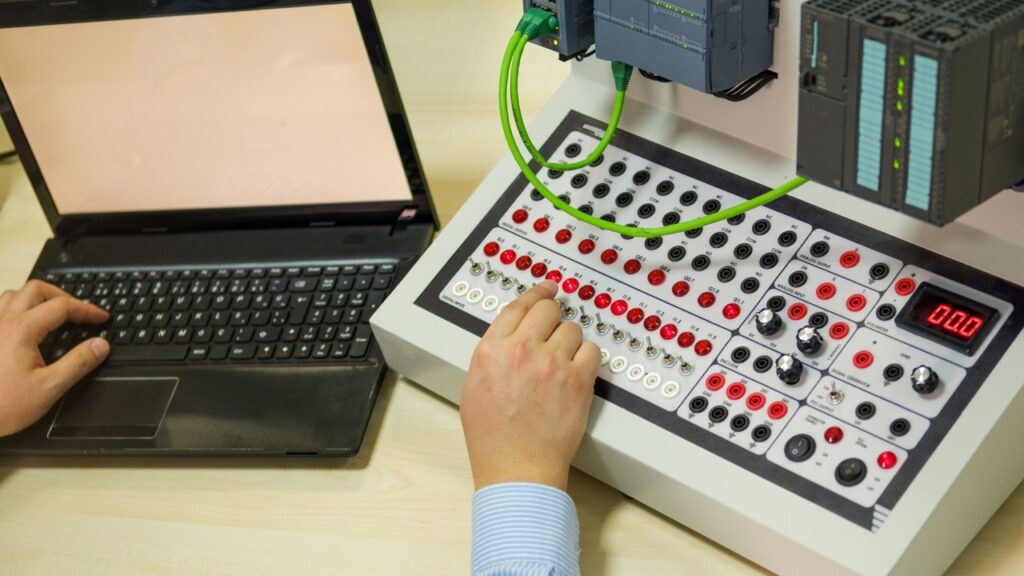

Designing Efficient I/O Systems
An effective I/O system design is crucial for the overall performance of a PLC application. Engineers must consider multiple factors, such as the number of inputs and outputs, response time requirements, and noise immunity. Implementing proper grounding and shielding techniques is essential to minimize electrical interference, thus enhancing the reliability of the PLC system.
Advanced I/O Concepts
Recent advancements in I/O technology have revolutionized PLC systems. High-speed communication protocols like EtherCAT and PROFINET have enabled more distributed and flexible I/O architectures. The integration of intelligent I/O modules has further allowed for decentralized control and improved diagnostic capabilities, making PLC systems more robust and easier to maintain.
Conclusion
Inputs and outputs are the fundamental building blocks of PLC systems. By understanding their roles and the factors influencing their design, engineers can develop more sophisticated and reliable automation solutions. As technology evolves, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of PLC I/O systems, paving the way for advanced industrial automation.